Page 100 - Teaching English at Primary Level: From Theory into the Classroom
P. 100
Reading and Writing
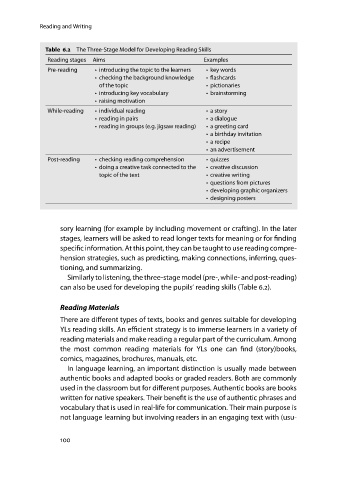
Table 6.2 The Three-Stage Model for Developing Reading Skills
Reading stages Aims Examples
Pre-reading • introducing the topic to the learners •key words
• checking the background knowledge • flashcards
of the topic • pictionaries
• introducing key vocabulary • brainstorming
• raising motivation
While-reading • individual reading •a story
• reading in pairs • a dialogue
• reading in groups (e.g. jigsaw reading) • a greeting card
• a birthday invitation
•a recipe
• an advertisement
Post-reading • checking reading comprehension •quizzes
• doing a creative task connected to the • creative discussion
topic of the text •creative writing
•questions from pictures
• developing graphic organizers
• designing posters
sory learning (for example by including movement or crafting). In the later
stages, learners will be asked to read longer texts for meaning or for finding
specific information. At this point, they can be taught to use reading compre-
hension strategies, such as predicting, making connections, inferring, ques-
tioning, and summarizing.
Similarlytolistening,thethree-stagemodel(pre-,while-andpost-reading)
can also be used for developing the pupils’ reading skills (Table 6.2).
Reading Materials
There are different types of texts, books and genres suitable for developing
YLs reading skills. An efficient strategy is to immerse learners in a variety of
reading materials and make reading a regular part of the curriculum. Among
the most common reading materials for YLs one can find (story)books,
comics, magazines, brochures, manuals, etc.
In language learning, an important distinction is usually made between
authentic books and adapted books or graded readers. Both are commonly
used in the classroom but for different purposes. Authentic books are books
written for native speakers. Their benefit is the use of authentic phrases and
vocabulary that is used in real-life for communication. Their main purpose is
not language learning but involving readers in an engaging text with (usu-
100