Page 17 - Koderman, Miha, and Vuk Tvrtko Opačić. Eds. 2020. Challenges of tourism development in protected areas of Croatia and Slovenia. Koper, Zagreb: University of Primorska Press, Croatian Geographical Society
P. 17
lanatory notes on tourism in protected areas of croatia and slovenia
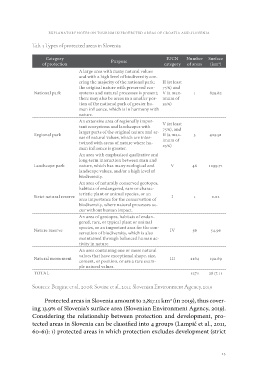
Tab. 3 Types of protected areas in Slovenia
Category Purpose IUCN Number Surface
of protection category of areas (km2)
National park 839.82
A large area with many natural values 1
Regional park and with a high level of biodiversity cov- 429.91
Landscape park ering the majority of the national park; II (at least 3 1299.71
Strict natural reserve the original nature with preserved eco- 75%) and 46
Nature reserve systems and natural processes is present; V (a max- 1 0.02
Natural monument there may also be areas in a smaller por- imum of 56 54.96
TOTAL tion of the national park of greater hu- 25%) 1164 192.69
man influence, which is in harmony with 1271 2817.11
nature.
An extensive area of regionally impor- V (at least
tant ecosystems and landscapes with 75%), and
larger parts of the original nature and ar- II (a max-
eas of natural values, which are inter- imum of
twined with areas of nature where hu- 25%)
man influence is greater.
An area with emphasised qualitative and V
long-term interaction between man and
nature, which has many ecological and
landscape values, and/or a high level of
biodiversity.
An area of naturally conserved geotopes, I
habitats of endangered, rare or charac-
teristic plant or animal species, or an
area importance for the conservation of
biodiversity, where natural processes oc-
cur without human impact.
An area of geotopes, habitats of endan- IV
gered, rare, or typical plant or animal
species, or an important area for the con-
servation of biodiversity, which is also
maintained through balanced human ac-
tivity in nature.
An area containing one or more natural III
values that have exceptional shape, size,
content, or position, or are a rare exam-
ple natural values.
Sources: Berginc et al., 2006; Sovinc et al., 2011; Slovenian Environment Agency, 2019
Protected areas in Slovenia amount to 2,817.11 km2 (in 2019), thus cover-
ing 13.9% of Slovenia’s surface area (Slovenian Environment Agency, 2019).
Considering the relationship between protection and development, pro-
tected areas in Slovenia can be classified into 4 groups (Lampič et al., 2011,
60-61): 1) protected areas in which protection excludes development (strict
15
Tab. 3 Types of protected areas in Slovenia
Category Purpose IUCN Number Surface
of protection category of areas (km2)
National park 839.82
A large area with many natural values 1
Regional park and with a high level of biodiversity cov- 429.91
Landscape park ering the majority of the national park; II (at least 3 1299.71
Strict natural reserve the original nature with preserved eco- 75%) and 46
Nature reserve systems and natural processes is present; V (a max- 1 0.02
Natural monument there may also be areas in a smaller por- imum of 56 54.96
TOTAL tion of the national park of greater hu- 25%) 1164 192.69
man influence, which is in harmony with 1271 2817.11
nature.
An extensive area of regionally impor- V (at least
tant ecosystems and landscapes with 75%), and
larger parts of the original nature and ar- II (a max-
eas of natural values, which are inter- imum of
twined with areas of nature where hu- 25%)
man influence is greater.
An area with emphasised qualitative and V
long-term interaction between man and
nature, which has many ecological and
landscape values, and/or a high level of
biodiversity.
An area of naturally conserved geotopes, I
habitats of endangered, rare or charac-
teristic plant or animal species, or an
area importance for the conservation of
biodiversity, where natural processes oc-
cur without human impact.
An area of geotopes, habitats of endan- IV
gered, rare, or typical plant or animal
species, or an important area for the con-
servation of biodiversity, which is also
maintained through balanced human ac-
tivity in nature.
An area containing one or more natural III
values that have exceptional shape, size,
content, or position, or are a rare exam-
ple natural values.
Sources: Berginc et al., 2006; Sovinc et al., 2011; Slovenian Environment Agency, 2019
Protected areas in Slovenia amount to 2,817.11 km2 (in 2019), thus cover-
ing 13.9% of Slovenia’s surface area (Slovenian Environment Agency, 2019).
Considering the relationship between protection and development, pro-
tected areas in Slovenia can be classified into 4 groups (Lampič et al., 2011,
60-61): 1) protected areas in which protection excludes development (strict
15