Page 182 - Teaching English at Primary Level: From Theory into the Classroom
P. 182
Basic Principles of Assessment
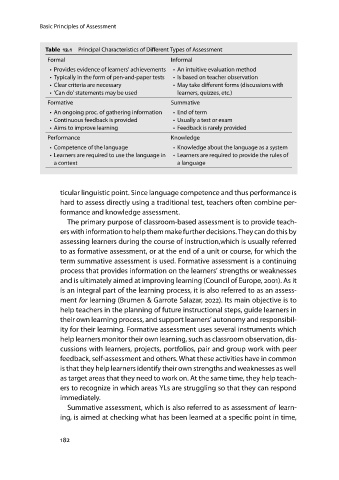
Table 12.1 Principal Characteristics of Different Types of Assessment
Formal Informal
• Provides evidence of learners’ achievements • An intuitive evaluation method
• Typically in the form of pen-and-paper tests • Is based on teacher observation
• Clear criteria are necessary • May take different forms (discussions with
• ‘Can do’ statements may be used learners, quizzes, etc.)
Formative Summative
• An ongoing proc. of gathering information •End of term
• Continuous feedback is provided • Usually a test or exam
• Aims to improve learning • Feedback is rarely provided
Performance Knowledge
• Competence of the language • Knowledge about the language as a system
• Learners are required to use the language in • Learners are required to provide the rules of
acontext a language
ticular linguistic point. Since language competence and thus performance is
hard to assess directly using a traditional test, teachers often combine per-
formance and knowledge assessment.
The primary purpose of classroom-based assessment is to provide teach-
erswith information to helpthemmakefurtherdecisions.Theycan do thisby
assessing learners during the course of instruction,which is usually referred
to as formative assessment, or at the end of a unit or course, for which the
term summative assessment is used. Formative assessment is a continuing
process that provides information on the learners’ strengths or weaknesses
and is ultimately aimed at improving learning (Council of Europe, 2001). As it
is an integral part of the learning process, it is also referred to as an assess-
ment for learning (Brumen & Garrote Salazar, 2022). Its main objective is to
help teachers in the planning of future instructional steps, guide learners in
their own learning process, and support learners’ autonomy and responsibil-
ity for their learning. Formative assessment uses several instruments which
help learners monitor their own learning, such as classroom observation, dis-
cussions with learners, projects, portfolios, pair and group work with peer
feedback, self-assessment and others. What these activities have in common
is that they help learners identify their own strengths and weaknesses as well
as target areas that they need to work on. At the same time, they help teach-
ers to recognize in which areas YLs are struggling so that they can respond
immediately.
Summative assessment, which is also referred to as assessment of learn-
ing, is aimed at checking what has been learned at a specific point in time,
182