Page 188 - Teaching English at Primary Level: From Theory into the Classroom
P. 188
Assessing Language Skills
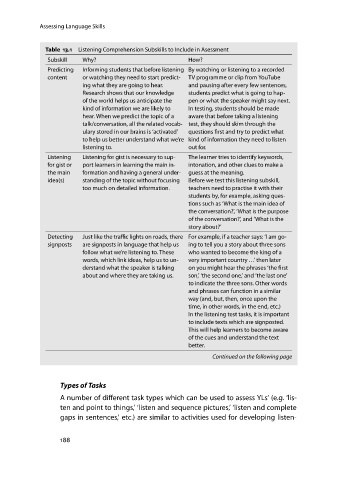
Table 13.1 Listening Comprehension Subskills to Include in Asessment
Subskill Why? How?
Predicting Informing students that before listening By watching or listening to a recorded
content or watching they need to start predict- TV programme or clip from YouTube
ing what they are going to hear. and pausing after every few sentences,
Research shows that our knowledge students predict what is going to hap-
of the world helps us anticipate the pen or what the speaker might say next.
kind of information we are likely to In testing, students should be made
hear. When we predict the topic of a aware that before taking a listening
talk/conversation, all the related vocab- test, they should skim through the
ulary stored in our brains is ‘activated’ questions first and try to predict what
to help us better understand what we’re kind of information they need to listen
listening to. out for.
Listening Listening for gist is necessary to sup- The learner tries to identify keywords,
for gist or port learners in learning the main in- intonation, and other clues to make a
the main formation and having a general under- guess at the meaning.
idea(s) standing of the topic without focusing Before we test this listening subskill,
too much on detailed information. teachers need to practise it with their
students by, for example, asking ques-
tions such as ‘What is the main idea of
the conversation?’, ‘What is the purpose
of the conversation?’, and ‘What is the
story about?’
Detecting Just like the traffic lights on roads, there Forexample,if a teachersays: ‘I am go-
signposts are signposts in language that help us ing to tell you a story about three sons
follow what we’re listening to. These who wanted to become the king of a
words, which link ideas, help us to un- very important country ...’ then later
derstand what the speaker is talking on you might hear the phrases ‘the first
about and where they are taking us. son,’‘thesecondone,’ and‘thelastone’
to indicate the three sons. Other words
and phrases can function in a similar
way (and, but, then, once upon the
time, in other words, in the end, etc.)
In the listening test tasks, it is important
to include texts which are signposted.
This will help learners to become aware
of the cues and understand the text
better.
Continued on the following page
Types of Tasks
A number of different task types which can be used to assess YLs’ (e.g. ‘lis-
ten and point to things,’ ‘listen and sequence pictures,’ ‘listen and complete
gaps in sentences,’ etc.) are similar to activities used for developing listen-
188