Page 74 - Teaching English at Primary Level: From Theory into the Classroom
P. 74
Listening and Speaking
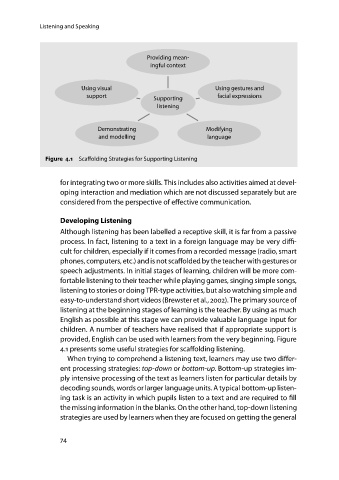
Providing mean-
ingful context
Using visual Using gestures and
support Supporting facial expressions
listening
Demonstrating Modifying
and modelling language
Figure 4.1 Scaffolding Strategies for Supporting Listening
for integrating two or more skills. This includes also activities aimed at devel-
oping interaction and mediation which are not discussed separately but are
considered from the perspective of effective communication.
Developing Listening
Although listening has been labelled a receptive skill, it is far from a passive
process. In fact, listening to a text in a foreign language may be very diffi-
cult for children, especially if it comes from a recorded message (radio, smart
phones,computers,etc.) andisnot scaffoldedbytheteacherwith gesturesor
speech adjustments. In initial stages of learning, children will be more com-
fortable listening to their teacher while playing games, singing simple songs,
listening to stories or doing TPR-type activities, but also watching simple and
easy-to-understand short videos (Brewster et al., 2002). The primary source of
listening at the beginning stages of learning is the teacher. By using as much
English as possible at this stage we can provide valuable language input for
children. A number of teachers have realised that if appropriate support is
provided, English can be used with learners from the very beginning. Figure
4.1 presents some useful strategies for scaffolding listening.
When trying to comprehend a listening text, learners may use two differ-
ent processing strategies: top-down or bottom-up. Bottom-up strategies im-
ply intensive processing of the text as learners listen for particular details by
decoding sounds, words or larger language units. A typical bottom-up listen-
ing task is an activity in which pupils listen to a text and are required to fill
the missing information in the blanks. On the other hand, top-down listening
strategies are used by learners when they are focused on getting the general
74