Page 12 - Petelin, Ana. 2024. Ed. Zdravje delovno aktivnih in starejših odraslih | Health of the Working-Age and Older Adults. Zbornik prispevkov z recenzijo | Proceedings. Koper: University of Primorska Press
P. 12
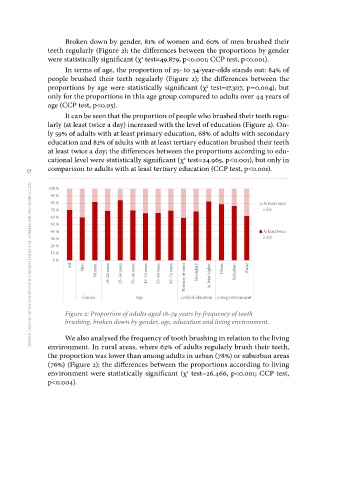
Broken down by gender, 81% of women and 60% of men brushed their
teeth regularly (Figure 2); the differences between the proportions by gender
were statistically significant (χ test=49.879, p<0.001; CCP test, p<0.001).
2
In terms of age, the proportion of 25- to 34-year-olds stands out: 84% of
people brushed their teeth regularly (Figure 2); the differences between the
proportions by age were statistically significant (χ test=17.307, p=0.004), but
2
only for the proportions in this age group compared to adults over 44 years of
age (CCP test, p<0.05).
It can be seen that the proportion of people who brushed their teeth regu-
larly (at least twice a day) increased with the level of education (Figure 2). On-
ly 59% of adults with at least primary education, 68% of adults with secondary
education and 82% of adults with at least tertiary education brushed their teeth
at least twice a day; the differences between the proportions according to edu-
cational level were statistically significant (χ test=24.965, p<0.001), but only in
2
comparison to adults with at least tertiary education (CCP test, p<0.001).
12
zdravje delovno aktivnih in starejših odraslih | health of working-age and older adults
100 %
90 %
80 % At most once
70 % a day
60 %
50 %
40 % At least twice
30 % a day
20 %
10 %
0 %
All Men Women 18–24 years 25–34 years 35–44 years 45–54 years 55–64 years 65–74 years Primary at most Secondary At least higher Urban Suburban Rural
Gender Age Level of education Living environment
Figure 2: Proportion of adults aged 18–74 years by frequency of tooth
brushing, broken down by gender, age, education and living environment.
We also analysed the frequency of tooth brushing in relation to the living
environment. In rural areas, where 62% of adults regularly brush their teeth,
the proportion was lower than among adults in urban (78%) or suburban areas
(76%) (Figure 2); the differences between the proportions according to living
environment were statistically significant (χ test=26.466, p<0.001; CCP test,
2
p<0.004).