Page 199 - Teaching English at Primary Level: From Theory into the Classroom
P. 199
Assessing Reading
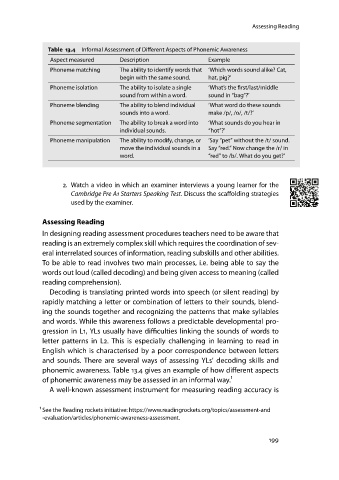
Table 13.4 Informal Assessment of Different Aspects of Phonemic Awareness
Aspect measured Description Example
Phoneme matching The ability to identify words that ‘Which words sound alike? Cat,
beginwiththe same sound. hat, pig?’
Phoneme isolation The ability to isolate a single ‘What’s the first/last/middle
sound from within a word. sound in “bag”?’
Phoneme blending The ability to blend individual ‘What word do these sounds
sounds into a word. make /p/, /o/, /t/?’
Phoneme segmentation The ability to break a word into ‘What sounds do you hear in
individual sounds. “hot”?’
Phoneme manipulation The ability to modify, change, or ‘Say “pet” without the /t/ sound.
move the individual sounds in a Say “red.” Now change the /r/ in
word. “red” to/b/. What doyou get?’
2. Watch a video in which an examiner interviews a young learner for the
Cambridge Pre A1 Starters Speaking Test. Discuss the scaffolding strategies
used by the examiner.
Assessing Reading
In designing reading assessment procedures teachers need to be aware that
reading is an extremely complex skill which requires the coordination of sev-
eral interrelated sources of information, reading subskills and other abilities.
To be able to read involves two main processes, i.e. being able to say the
words out loud (called decoding) and being given access to meaning (called
reading comprehension).
Decoding is translating printed words into speech (or silent reading) by
rapidly matching a letter or combination of letters to their sounds, blend-
ing the sounds together and recognizing the patterns that make syllables
and words. While this awareness follows a predictable developmental pro-
gression in L1, YLs usually have difficulties linking the sounds of words to
letter patterns in L2. This is especially challenging in learning to read in
English which is characterised by a poor correspondence between letters
and sounds. There are several ways of assessing YLs’ decoding skills and
phonemic awareness. Table 13.4 gives an example of how different aspects
of phonemic awareness may be assessed in an informal way.¹
A well-known assessment instrument for measuring reading accuracy is
¹ See the Reading rockets initiative: https://www.readingrockets.org/topics/assessment-and
-evaluation/articles/phonemic-awareness-assessment.
199