Page 20 - Teaching English at Primary Level: From Theory into the Classroom
P. 20
Key Principles
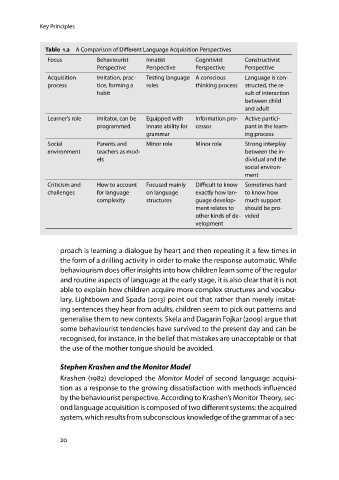
Table 1.2 A Comparison of Different Language Acquisition Perspectives
Focus Behaviourist Innatist Cognitivist Constructivist
Perspective Perspective Perspective Perspective
Acquisition Imitation, prac- Testing language Aconscious Language is con-
process tice, forming a rules thinking process structed, the re-
habit sult of interaction
between child
and adult
Learner’s role Imitator, can be Equipped with Information pro- Active partici-
programmed innate ability for cessor pant in the learn-
grammar ing process
Social Parents and Minor role Minor role Strong interplay
environment teachers as mod- between the in-
els dividual and the
social environ-
ment
Criticism and How to account Focused mainly Difficult to know Sometimes hard
challenges for language on language exactly how lan- to know how
complexity structures guage develop- much support
ment relates to should be pro-
other kinds of de- vided
velopment
proach is learning a dialogue by heart and then repeating it a few times in
the form of a drilling activity in order to make the response automatic. While
behaviourism does offer insights into how children learn some of the regular
and routine aspects of language at the early stage, it is also clear that it is not
able to explain how children acquire more complex structures and vocabu-
lary. Lightbown and Spada (2013) point out that rather than merely imitat-
ing sentences they hear from adults, children seem to pick out patterns and
generalise them to new contexts. Skela and Dagarin Fojkar (2009) argue that
some behaviourist tendencies have survived to the present day and can be
recognised, for instance, in the belief that mistakes are unacceptable or that
the use of the mother tongue should be avoided.
Stephen Krashen and the Monitor Model
Krashen (1982) developed the Monitor Model of second language acquisi-
tion as a response to the growing dissatisfaction with methods influenced
by the behaviourist perspective. According to Krashen’s Monitor Theory, sec-
ond language acquisition is composed of two different systems: the acquired
system,which resultsfromsubconsciousknowledgeofthegrammarofasec-
20