Page 23 - Teaching English at Primary Level: From Theory into the Classroom
P. 23
The Behaviourist Perspective
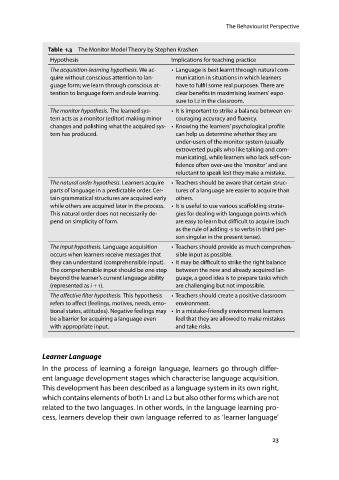
Table 1.3 The Monitor Model Theory by Stephen Krashen
Hypothesis Implications for teaching practice
The acquisition-learning hypothesis. We ac- • Language is best learnt through natural com-
quire without conscious attention to lan- munication in situations in which learners
guage form; we learn through conscious at- have to fulfil some real purposes.•There are
tention to language form and rule learning. clear benefits in maximising learners’ expo-
sure to L2 in the classroom.
The monitor hypothesis. The learned sys- • It is important to strike a balance between en-
tem acts as a monitor (editor) making minor couraging accuracy and fluency.
changes and polishing what the acquired sys- • Knowing the learners’ psychological profile
tem has produced. can help us determine whether they are
under-users of the monitor system (usually
extroverted pupils who like talking and com-
municating), while learners who lack self-con-
fidence often over-use the ‘monitor’ and are
reluctant to speak lest they make a mistake.
The natural order hypothesis. Learners acquire • Teachers should be aware that certain struc-
parts of language in a predictable order. Cer- tures of a language are easier to acquire than
tain grammatical structures are acquired early others.
while others are acquired later in the process. • It is useful to use various scaffolding strate-
This natural order does not necessarily de- gies for dealing with language points which
pend on simplicity of form. are easy to learn but difficult to acquire (such
as the rule of adding -s to verbs in third per-
son singular in the present tense).
The input hypothesis. Language acquisition • Teachers should provide as much comprehen-
occurs when learners receive messages that sible input as possible.
they can understand (comprehensible input). • It may be difficult to strike the right balance
The comprehensible input should be one step between the new and already acquired lan-
beyond the learner’s current language ability guage, a good idea is to prepare tasks which
(represented as i +1). are challenging but not impossible.
The affective filter hypothesis. This hypothesis • Teachers should create a positive classroom
refers to affect (feelings, motives, needs, emo- environment.
tional states, attitudes). Negative feelings may • In a mistake-friendly environment learners
be a barrier for acquiring a language even feel that they are allowed to make mistakes
with appropriate input. and take risks.
Learner Language
In the process of learning a foreign language, learners go through differ-
ent language development stages which characterise language acquisition.
This development has been described as a language system in its own right,
whichcontainselementsofbothL1and L2 butalsoother formswhich arenot
related to the two languages. In other words, in the language learning pro-
cess, learners develop their own language referred to as ‘learner language’
23