Page 34 - Teaching English at Primary Level: From Theory into the Classroom
P. 34
Approaches to Language Teaching
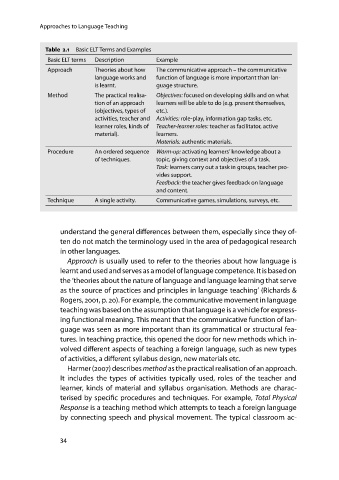
Table 2.1 Basic ELT Terms and Examples
Basic ELT terms Description Example
Approach Theories about how The communicative approach – the communicative
language works and function of language is more important than lan-
is learnt. guage structure.
Method The practical realisa- Objectives: focused on developing skills and on what
tion of an approach learners will be able to do (e.g. present themselves,
(objectives, types of etc.).
activities, teacher and Activities: role-play, information gap tasks, etc.
learner roles, kinds of Teacher-learner roles: teacher as facilitator, active
material). learners.
Materials: authentic materials.
Procedure An ordered sequence Warm-up: activating learners’ knowledge about a
of techniques. topic, giving context and objectives of a task.
Task: learners carry out a task in groups, teacher pro-
vides support.
Feedback: the teacher gives feedback on language
and content.
Technique A single activity. Communicative games, simulations, surveys, etc.
understand the general differences between them, especially since they of-
ten do not match the terminology used in the area of pedagogical research
in other languages.
Approach is usually used to refer to the theories about how language is
learntandusedandservesasamodeloflanguagecompetence.Itisbasedon
the ‘theories about the nature of language and language learning that serve
as the source of practices and principles in language teaching’ (Richards &
Rogers, 2001, p. 20). For example, the communicative movement in language
teaching was based on the assumption that language is a vehicle for express-
ing functional meaning. This meant that the communicative function of lan-
guage was seen as more important than its grammatical or structural fea-
tures. In teaching practice, this opened the door for new methods which in-
volved different aspects of teaching a foreign language, such as new types
of activities, a different syllabus design, new materials etc.
Harmer(2007) describes method asthepracticalrealisation ofan approach.
It includes the types of activities typically used, roles of the teacher and
learner, kinds of material and syllabus organisation. Methods are charac-
terised by specific procedures and techniques. For example, Total Physical
Response is a teaching method which attempts to teach a foreign language
by connecting speech and physical movement. The typical classroom ac-
34