Page 85 - Štemberger Tina, Čotar Konrad Sonja, Rutar Sonja, Žakelj Amalija. Ur. 2022. Oblikovanje inovativnih učnih okolij. Koper: Založba Univerze na Primorskem
P. 85
Need for ICT Use in Classroom as a Response to Cognitive Style Change in Children
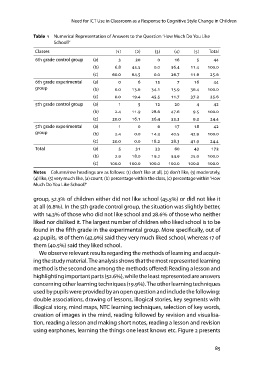
Table 1 Numerical Representation of Answers to the Question ‘How Much Do You Like
School?’
Classes () () () () () Total
th grade control group (a)
(b) . . . . . .
th grade experimental (c) . . . . .
group (a) .
th grade control group (b) .
(c) . . . . .
th grade experimental (a) . . . . .
group (b) . .
Total (c) .
(a) . . . .
(b) . . . . .
(c) . .
(a) . .
(b) . . . .
(c) . . . .
. . .
. . .
. . .
. . .
.
Notes Column/row headings are as follows: (1) don’t like at all, (2) don’t like, (3) moderately,
(4) like, (5) very much like, (a) count, (b) percentage within the class, (c) percentage within ‘How
Much Do You Like School?’
group, 52.3 of children either did not like school (45.5) or did not like it
at all (6.8). In the 5th grade control group, the situation was slightly better,
with 14.3 of those who did not like school and 28.6 of those who neither
liked nor disliked it. The largest number of children who liked school is to be
found in the fifth grade in the experimental group. More specifically, out of
42 pupils, 18 of them (42.9) said they very much liked school, whereas 17 of
them (40.5) said they liked school.
We observe relevant results regarding the methods of learning and acquir-
ing the study material. The analysis shows that the most represented learning
method is the second one among the methods offered: Reading a lesson and
highlighting important parts (52.6), while the least represented are answers
concerning other learning techniques (19.9). The other learning techniques
used by pupils were provided by an open question and include the following:
double associations, drawing of lessons, illogical stories, key segments with
illogical story, mind maps, NTC learning techniques, selection of key words,
creation of images in the mind, reading followed by revision and visualisa-
tion, reading a lesson and making short notes, reading a lesson and revision
using earphones, learning the things one least knows etc. Figure 2 presents
85
Table 1 Numerical Representation of Answers to the Question ‘How Much Do You Like
School?’
Classes () () () () () Total
th grade control group (a)
(b) . . . . . .
th grade experimental (c) . . . . .
group (a) .
th grade control group (b) .
(c) . . . . .
th grade experimental (a) . . . . .
group (b) . .
Total (c) .
(a) . . . .
(b) . . . . .
(c) . .
(a) . .
(b) . . . .
(c) . . . .
. . .
. . .
. . .
. . .
.
Notes Column/row headings are as follows: (1) don’t like at all, (2) don’t like, (3) moderately,
(4) like, (5) very much like, (a) count, (b) percentage within the class, (c) percentage within ‘How
Much Do You Like School?’
group, 52.3 of children either did not like school (45.5) or did not like it
at all (6.8). In the 5th grade control group, the situation was slightly better,
with 14.3 of those who did not like school and 28.6 of those who neither
liked nor disliked it. The largest number of children who liked school is to be
found in the fifth grade in the experimental group. More specifically, out of
42 pupils, 18 of them (42.9) said they very much liked school, whereas 17 of
them (40.5) said they liked school.
We observe relevant results regarding the methods of learning and acquir-
ing the study material. The analysis shows that the most represented learning
method is the second one among the methods offered: Reading a lesson and
highlighting important parts (52.6), while the least represented are answers
concerning other learning techniques (19.9). The other learning techniques
used by pupils were provided by an open question and include the following:
double associations, drawing of lessons, illogical stories, key segments with
illogical story, mind maps, NTC learning techniques, selection of key words,
creation of images in the mind, reading followed by revision and visualisa-
tion, reading a lesson and making short notes, reading a lesson and revision
using earphones, learning the things one least knows etc. Figure 2 presents
85