Page 235 - Hojnik, Jana. 2017. In Persuit of Eco-innovation. Drivers and Consequences of Eco-innovation at Firm Level. Koper: University of Primorska Press
P. 235
Eco-innovation models
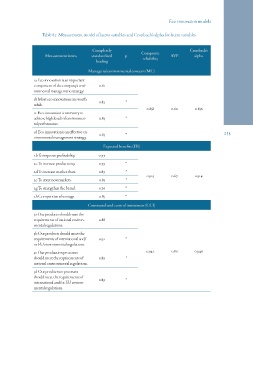
Table 82: Measurement model of latent variables and Cronbach’s alpha for latent variables
Measurement items Completely p Composite AVE Cronbach’s
standardized reliability alpha
loading
Managerial environmental concern (MC)
1a Eco-innovation is an important 0.61
component of the company’s envi-
ronmental management strategy.
1b Most eco-innovations are worth- 0.82 *
while.
0.858 0.60 0.836
1c Eco-innovation is necessary to
achieve high levels of environmen- 0.83 *
tal performance.
1d Eco-innovation is an effective en- 0.83 * 235
vironmental management strategy.
Expected benefits (EB)
2b To improve profitability. 0.77
2c To increase productivity. 0.79 *
2d To increase market share. 0.89 *
2e To enter new markets.
2g To strengthen the brand. 0.923 0.67 0.914
2h Competitive advantage. 0.83 *
0.76 *
0.85 *
Command-and-control instrument (CCI)
3a Our products should meet the 0.88
requirements of national environ-
mental regulations.
3b Our products should meet the 0.92 *
requirements of international and/ 0.89
or EU environmental regulations. 0.942 0.80 0.946
*
3c Our production processes
should meet the requirements of
national environmental regulations.
3d Our production processes 0.89 *
should meet the requirements of
international and/or EU environ-
mental regulations.
Table 82: Measurement model of latent variables and Cronbach’s alpha for latent variables
Measurement items Completely p Composite AVE Cronbach’s
standardized reliability alpha
loading
Managerial environmental concern (MC)
1a Eco-innovation is an important 0.61
component of the company’s envi-
ronmental management strategy.
1b Most eco-innovations are worth- 0.82 *
while.
0.858 0.60 0.836
1c Eco-innovation is necessary to
achieve high levels of environmen- 0.83 *
tal performance.
1d Eco-innovation is an effective en- 0.83 * 235
vironmental management strategy.
Expected benefits (EB)
2b To improve profitability. 0.77
2c To increase productivity. 0.79 *
2d To increase market share. 0.89 *
2e To enter new markets.
2g To strengthen the brand. 0.923 0.67 0.914
2h Competitive advantage. 0.83 *
0.76 *
0.85 *
Command-and-control instrument (CCI)
3a Our products should meet the 0.88
requirements of national environ-
mental regulations.
3b Our products should meet the 0.92 *
requirements of international and/ 0.89
or EU environmental regulations. 0.942 0.80 0.946
*
3c Our production processes
should meet the requirements of
national environmental regulations.
3d Our production processes 0.89 *
should meet the requirements of
international and/or EU environ-
mental regulations.