Page 237 - Hojnik, Jana. 2017. In Persuit of Eco-innovation. Drivers and Consequences of Eco-innovation at Firm Level. Koper: University of Primorska Press
P. 237
Eco-innovation models
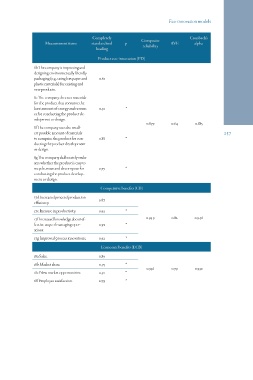
Measurement items Completely p Composite AVE Cronbach’s
standardized reliability alpha
loading
Product eco-innovation (PD)
8b The company is improving and 0.61 * 237
designing environmentally friendly 0.91 0.879 0.64 0.885
packaging (e.g., using less paper and 0.88
plastic materials) for existing and 0.79 *
new products.
*
8e The company chooses materials
for the product that consume the
least amount of energy and resourc-
es for conducting the product de-
velopment or design.
8f The company uses the small-
est possible amount of materials
to comprise the product for con-
ducting the product development
or design.
8g The company deliberately evalu-
ates whether the product is easy to
recycle, reuse and decompose for
conducting the product develop-
ment or design.
Competitive benefits (CB)
17d Increased process/production 0.87
efficiency.
17e Increase in productivity. 0.92 *
0.92 0.949 0.82 0.946
17f Increased knowledge about ef-
fective ways of managing oper- *
ations.
17g Improved process innovations. 0.92 *
Economic benefits (ECB)
18a Sales. 0.89 *
18b Market share. 0.95 0.936 0.79 0.930
18c New market opportunities. 0.91
18f Employee satisfaction. 0.79 *
*
Measurement items Completely p Composite AVE Cronbach’s
standardized reliability alpha
loading
Product eco-innovation (PD)
8b The company is improving and 0.61 * 237
designing environmentally friendly 0.91 0.879 0.64 0.885
packaging (e.g., using less paper and 0.88
plastic materials) for existing and 0.79 *
new products.
*
8e The company chooses materials
for the product that consume the
least amount of energy and resourc-
es for conducting the product de-
velopment or design.
8f The company uses the small-
est possible amount of materials
to comprise the product for con-
ducting the product development
or design.
8g The company deliberately evalu-
ates whether the product is easy to
recycle, reuse and decompose for
conducting the product develop-
ment or design.
Competitive benefits (CB)
17d Increased process/production 0.87
efficiency.
17e Increase in productivity. 0.92 *
0.92 0.949 0.82 0.946
17f Increased knowledge about ef-
fective ways of managing oper- *
ations.
17g Improved process innovations. 0.92 *
Economic benefits (ECB)
18a Sales. 0.89 *
18b Market share. 0.95 0.936 0.79 0.930
18c New market opportunities. 0.91
18f Employee satisfaction. 0.79 *
*