Page 217 - Čotar Konrad Sonja, Borota Bogdana, Rutar Sonja, Drljić Karmen, Jelovčan Giuliana. Ur. 2022. Vzgoja in izobraževanje predšolskih otrok prvega starostnega obdobja. Koper: Založba Univerze na Primorskem
P. 217
Quality of Life of Families of Early Aged Children with Disabilities
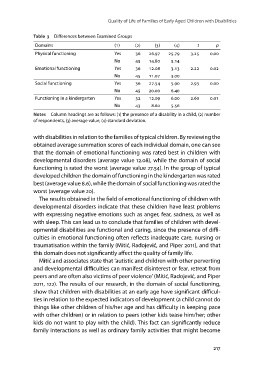
Table 3 Differences between Examined Groups
Domains () () () () tp
Physical functioning Yes . . . .
Emotional functioning No . .
Social functioning Yes . . . .
Functioning in a kindergarten No . .
Yes . . . .
No . .
Yes . . . .
No . .
Notes Column headings are as follows: (1) the presence of a disability in a child, (2) number
of respondents, (3) average value, (4) standard deviation.
with disabilities in relation to the families of typical children. By reviewing the
obtained average summation scores of each individual domain, one can see
that the domain of emotional functioning was rated best in children with
developmental disorders (average value 12.08), while the domain of social
functioning is rated the worst (average value 27.54). In the group of typical
developed children the domain of functioning in the kindergarten was rated
best (average value 8.6), while the domain of social functioning was rated the
worst (average value 20).
The results obtained in the field of emotional functioning of children with
developmental disorders indicate that these children have least problems
with expressing negative emotions such as anger, fear, sadness, as well as
with sleep. This can lead us to conclude that families of children with devel-
opmental disabilities are functional and caring, since the presence of diffi-
culties in emotional functioning often reflects inadequate care, nursing or
traumatisation within the family (Mitić, Radojević, and Piper 2011), and that
this domain does not significantly affect the quality of family life.
Mitić and associates state that ‘autistic and children with other perverting
and developmental difficulties can manifest disinterest or fear, retreat from
peers and are often also victims of peer violence’ (Mitić, Radojević, and Piper
2011, 122). The results of our research, in the domain of social functioning,
show that children with disabilities at an early age have significant difficul-
ties in relation to the expected indicators of development (a child cannot do
things like other children of his/her age and has difficulty in keeping pace
with other children) or in relation to peers (other kids tease him/her; other
kids do not want to play with the child). This fact can significantly reduce
family interactions as well as ordinary family activities that might become
217
Table 3 Differences between Examined Groups
Domains () () () () tp
Physical functioning Yes . . . .
Emotional functioning No . .
Social functioning Yes . . . .
Functioning in a kindergarten No . .
Yes . . . .
No . .
Yes . . . .
No . .
Notes Column headings are as follows: (1) the presence of a disability in a child, (2) number
of respondents, (3) average value, (4) standard deviation.
with disabilities in relation to the families of typical children. By reviewing the
obtained average summation scores of each individual domain, one can see
that the domain of emotional functioning was rated best in children with
developmental disorders (average value 12.08), while the domain of social
functioning is rated the worst (average value 27.54). In the group of typical
developed children the domain of functioning in the kindergarten was rated
best (average value 8.6), while the domain of social functioning was rated the
worst (average value 20).
The results obtained in the field of emotional functioning of children with
developmental disorders indicate that these children have least problems
with expressing negative emotions such as anger, fear, sadness, as well as
with sleep. This can lead us to conclude that families of children with devel-
opmental disabilities are functional and caring, since the presence of diffi-
culties in emotional functioning often reflects inadequate care, nursing or
traumatisation within the family (Mitić, Radojević, and Piper 2011), and that
this domain does not significantly affect the quality of family life.
Mitić and associates state that ‘autistic and children with other perverting
and developmental difficulties can manifest disinterest or fear, retreat from
peers and are often also victims of peer violence’ (Mitić, Radojević, and Piper
2011, 122). The results of our research, in the domain of social functioning,
show that children with disabilities at an early age have significant difficul-
ties in relation to the expected indicators of development (a child cannot do
things like other children of his/her age and has difficulty in keeping pace
with other children) or in relation to peers (other kids tease him/her; other
kids do not want to play with the child). This fact can significantly reduce
family interactions as well as ordinary family activities that might become
217