Page 33 - Volk, Marina, Štemberger, Tina, Sila, Anita, Kovač, Nives. Ur. 2021. Medpredmetno povezovanje: pot do uresničevanja vzgojno-izobraževalnih ciljev. Koper: Založba Univerze na Primorskem
P. 33
Changing the Educational Paradigm by Applying STEM Competencies
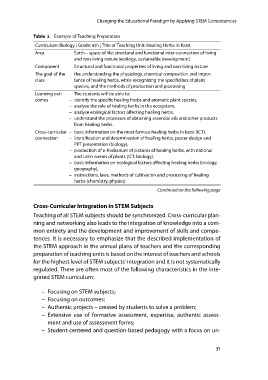
Table 2 Example of Teaching Preparation
Curriculum: Biology | Grade: 8th | Title of Teaching Unit: Healing Herbs in Karst
Area Earth – space of life: structural and functional inter-connection of living
and non-living nature (ecology, sustainable development)
Component Structural and functional properties of living and non-living nature
The goal of the the understanding the physiology, chemical composition and impor-
class tance of healing herbs, while recognizing the specificities of plant
species, and the methods of production and processing
Learning out- The students will be able to:
comes – identify the specific healing herbs and aromatic plant species,
– analyze the role of healing herbs in the ecosystem,
– analyze ecological factors affecting healing herbs,
– understand the processes of obtaining essential oils and other products
from healing herbs.
Cross-curricular – basic information on the most famous healing herbs in karst (ICT),
connection – identification and determination of healing herbs, poster design and
PPT presentation (biology),
– production of e-herbarium of pictures of healing herbs, with national
and Latin names of plants (ICT, biology),
– basic information on ecological factors affecting healing herbs (biology,
geography),
– instructions, laws, methods of cultivation and processing of healing
herbs (chemistry, physics)
Continued on the following page
Cross-Curricular Integration in STEM Subjects
Teaching of all STEM subjects should be synchronized. Cross-curricular plan-
ning and networking also leads to the integration of knowledge into a com-
mon entirety and the development and improvement of skills and compe-
tences. It is necessary to emphasize that the described implementation of
the STEM approach in the annual plans of teachers and the corresponding
preparation of teaching units is based on the interest of teachers and schools
for the highest level of STEM subjects’ integration and it is not systematically
regulated. There are often most of the following characteristics in the inte-
grated STEM curriculum:
– Focusing on STEM subjects;
– Focusing on outcomes;
– Authentic projects – created by students to solve a problem;
– Extensive use of formative assessment, expertise, authentic assess-
ment and use of assessment forms;
– Student-centered and question-based pedagogy with a focus on un-
31
Table 2 Example of Teaching Preparation
Curriculum: Biology | Grade: 8th | Title of Teaching Unit: Healing Herbs in Karst
Area Earth – space of life: structural and functional inter-connection of living
and non-living nature (ecology, sustainable development)
Component Structural and functional properties of living and non-living nature
The goal of the the understanding the physiology, chemical composition and impor-
class tance of healing herbs, while recognizing the specificities of plant
species, and the methods of production and processing
Learning out- The students will be able to:
comes – identify the specific healing herbs and aromatic plant species,
– analyze the role of healing herbs in the ecosystem,
– analyze ecological factors affecting healing herbs,
– understand the processes of obtaining essential oils and other products
from healing herbs.
Cross-curricular – basic information on the most famous healing herbs in karst (ICT),
connection – identification and determination of healing herbs, poster design and
PPT presentation (biology),
– production of e-herbarium of pictures of healing herbs, with national
and Latin names of plants (ICT, biology),
– basic information on ecological factors affecting healing herbs (biology,
geography),
– instructions, laws, methods of cultivation and processing of healing
herbs (chemistry, physics)
Continued on the following page
Cross-Curricular Integration in STEM Subjects
Teaching of all STEM subjects should be synchronized. Cross-curricular plan-
ning and networking also leads to the integration of knowledge into a com-
mon entirety and the development and improvement of skills and compe-
tences. It is necessary to emphasize that the described implementation of
the STEM approach in the annual plans of teachers and the corresponding
preparation of teaching units is based on the interest of teachers and schools
for the highest level of STEM subjects’ integration and it is not systematically
regulated. There are often most of the following characteristics in the inte-
grated STEM curriculum:
– Focusing on STEM subjects;
– Focusing on outcomes;
– Authentic projects – created by students to solve a problem;
– Extensive use of formative assessment, expertise, authentic assess-
ment and use of assessment forms;
– Student-centered and question-based pedagogy with a focus on un-
31